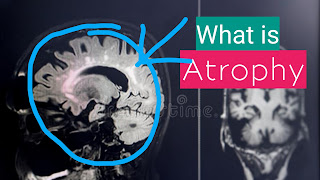
What is atrophy??
Atrophy is the shrinkage in the size of the cell by loss of cell substance.
Types or classification of atrophy
Physical atrophy
- Atrophy during early fetal development :example-atrophy of notochord & thyroglossal duct.
- Uterus decreases in size shortly after delivery.
Pathological atrophy
- Localized atrophy
- Ischaemic ateophy
- Disuse atrophy.
- Neuropathic atrophy in lower motor neuron lesion.
- Pressure atrophy.
- Hormonal atrophy.
2. Generalized atrophy :example-
- Decreased workload ( diause atrophy) : example - skeletal muscle atrophy due to restriction of complete bed rest or when a fractured bone is immobilized in a plaster cast.
- Lose of innervation ( denervation atrophy) : example -atrophy of the muacle fibers due to damage of the supplying nerves.
- Diminished blood supply :example- brain undergoes progressive atrophy due to atherosclerosis in cerebral vessels.
- Inadequate nutrition: example - marked skeletal muscle wasting ( cachexia) in profound protein -calorie malnutrition , chronic inflammation,cancer etc.
- Lose of endocrine stimulation : example - loss of oestrogen stimulation after menopause results in physiologic atrophy of the endometrium,vagainal epithelium & breast.
- Aging ( senile atrophy) : seen in the brain & heart.
- Pressure atrophy : Atrophy occurs due to tissue compression for a long time, example - enlarging benign tumor can cause atrophy in the surrounding compressed tissues.






Leave a Comment